Gemini, Chat GPT, large language models – what does it all mean for mortgage intermediaries?

If I asked Dall-e to draw me a picture of a cat juggling nine balls in the style of a French impressionist, it would do so in seconds. And once done, that painting would be far better than anything I could possibly hope to do. But, it wouldn’t be perfect – because it would appear that Chat GPT’s artistic side is too right-brained to actually count balls.
 Artificial Intelligence (AI) is advancing at an unprecedented pace, transforming various industries and redefining traditional roles. The mortgage intermediary profession will be no exception. As AI systems continue to develop, they are outperforming humans in specific tasks, compelling professionals to rethink their strategies and adapt to these technological shifts. If someone invents the steam powered weaving loom, learn how to work the loom, don’t be a weaver.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is advancing at an unprecedented pace, transforming various industries and redefining traditional roles. The mortgage intermediary profession will be no exception. As AI systems continue to develop, they are outperforming humans in specific tasks, compelling professionals to rethink their strategies and adapt to these technological shifts. If someone invents the steam powered weaving loom, learn how to work the loom, don’t be a weaver.
AI’s superior capabilities
Recent studies have highlighted several areas where AI surpasses human performance. According to Stanford University’s new 2024 AI Index Report, AI excels in image classification, visual reasoning, language comprehension, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics. These capabilities enable AI to perform tasks more efficiently and accurately than humans, especially in repetitive and data-intensive areas.
For instance, AI systems like GPT-4 and Gemini can generate fluent text, understand complex language nuances, and process audio. These multimodal abilities have allowed AI to handle customer inquiries, generate detailed reports, and create personalised communications for clients. Additionally, AI’s pattern recognition and predictive analytics are already being used for risk assessment, property valuation, and fraud detection in the mortgage industry.
Case studies in financial services
A recent paper by Andrew W. Lo and Jillian Ross from MIT discussed the role of Generative AI in financial advice, indicating that AI could convincingly role-play as a financial advisor. They noted, “An LLM (Large Language Model) can roleplay a financial advisor convincingly and often accurately for a client.” This revelation is concerning for the mortgage sector, where client social interaction plays a crucial role. Could AI pretend to be as likeable as you actually are?
However, Lo and Ross also cautioned that AI lacks the sense of responsibility and ethics required by law from a human financial advisor. This caveat underscores the importance of human oversight in AI applications, ensuring that ethical standards and responsibilities are upheld.
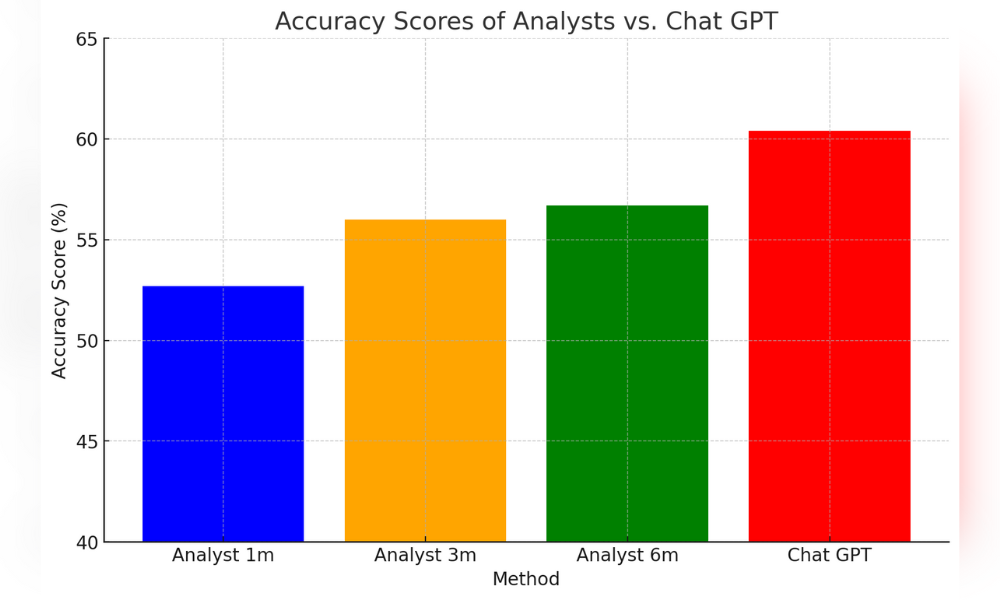
In another recent study from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business by Alex G. Kim, Maximilian Muhn, and Valeri V. Nikolaev, they revealed that GPT-4 could outperform human financial analysts in predicting earnings changes from financial statements. Using Chat GPT-4 Turbo, the researchers anonymized data and found that AI’s accuracy was significantly higher than that of human analysts. They concluded that trading strategies based on GPT-4’s predictions yielded higher Sharpe ratios and alphas compared to traditional models, indicating superior risk-adjusted returns.
Implications for mortgage intermediaries
The advancements in AI have profound implications for the mortgage industry. Here are some key areas where AI will impact our roles:
- Enhanced decision-making: AI tools can provide brokers with deeper insights into market trends, borrower creditworthiness, and loan product suitability. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making and allows brokers to offer more competitive and tailored loan options.
- Improved customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine inquiries, schedule appointments, and provide preliminary information to clients. This allows brokers to focus on more complex and personalized aspects of customer service. According to a study by McKinsey, AI can reduce the time spent on document verification by intermediaries by up to 50%. M-Powered already says that 60% of intermediary enquiries are solved by AI chatbots – some people may find them very frustrating, but in any event, M-Powered have freed up staff to help in other areas.
- Automation of administrative tasks: Many administrative tasks, such as document verification, data entry, and compliance checks, can be automated using AI. This reduces the time brokers spend on paperwork, allowing us to allocate more time to client engagement and business development.
- Risk Management and fraud detection: AI’s pattern recognition capabilities enhance the ability to detect anomalies and potential fraud in loan applications. This increases the overall security and reliability of the mortgage process.
- Complementary analysis: Despite AI’s capabilities, human judgment remains crucial. The combination of AI’s analytical power and human intuition can lead to better outcomes. Brokers can use AI to supplement their expertise, providing a more comprehensive advisory service.
Future prospects
The integration of AI into the mortgage industry is inevitable. As AI technology evolves, as mortgage intermediaries we must adapt and leverage these tools to enhance our services. While AI can handle complex numerical analyses intermediaries can focus on strategic advisory services, client relationship management, and personalised advice.
Studies indicate that clients still prefer advice from real people, but this preference may shift as AI becomes more sophisticated and trustworthy. Those of us who embrace AI and use it to complement their services will be better positioned to thrive in the future.
But what’s available now?
Major Large Language Model (LLM) AI online systems: strengths and weaknesses
Here is a list of some of the most prominent Large Language Model (LLM) AI systems currently available online, along with their major strengths and weaknesses:
1. GPT-4 (OpenAI)
Strengths:
- Highly advanced language inderstanding: Capable of understanding and generating human-like text across various domains.
- Multimodal capabilities: Can process both text and images, making it versatile for different applications.
- Wide adoption: Integrated into numerous applications and platforms, ensuring constant updates and improvements.
- High accuracy: Demonstrates superior performance in tasks like text generation, summarization, and translation.
Weaknesses:
- Resource Intensive: Requires significant computational resources, which can be costly.
- Ethical and bias concerns: Can generate biased or inappropriate content, necessitating careful oversight and filtering.
- Dependence on quality of prompts: Output quality can vary greatly depending on the input prompts.
Strengths:
- Focus on safety and ethics: Designed with safety and ethical considerations in mind, reducing the likelihood of harmful outputs.
- Robust conversational abilities: Excels in maintaining context and coherence in long conversations.
- User customizability: Allows users to fine-tune responses according to specific needs and preferences.
Weaknesses:
- Less versatile than GPT-4: While strong in conversation, it may not perform as well in other complex tasks like technical writing or code generation.
- Limited integration: Not as widely integrated into third-party applications compared to some competitors.
3. Gemini (Google DeepMind)
Strengths:
- Strong multimodal capabilities: Excels in both text and image processing, providing a comprehensive tool for various applications.
- Extensive training data: Trained on vast datasets, contributing to its accuracy and versatility.
- Integration with Google ecosystem: Seamless integration with Google’s suite of products and services.
Weaknesses:
- Privacy concerns: Being part of Google, there are concerns about data privacy and how user data is utilised.
- Resource requirements: Similar to GPT-4, it requires substantial computational power for optimal performance.
4. LLaMA (Meta)
Strengths:
- Open-source model: Available for public use, allowing for extensive customization and experimentation by researchers and developers.
- Efficient performance: Designed to be more efficient, requiring less computational power compared to some other LLMs.
- Strong community support: The open-source nature has fostered a robust community of users and contributors.
Weaknesses:
- Less polished: As an open-source project, it may lack the polish and support of more commercial models.
- Security risks: Open-source models can be more susceptible to misuse or exploitation.
5. Ernie (Baidu)
Strengths:
- Strong in Chinese language processing: Excels in tasks involving the Chinese language, making it ideal for applications in Chinese-speaking regions.
- Integrated with Baidu services: Seamlessly integrates with Baidu’s ecosystem, enhancing its utility for users of Baidu products.
Weaknesses:
- Limited global reach: Primarily focused on the Chinese market, with less support for other languages and regions.
- Regulatory issues: Operating in China means it is subject to stringent government regulations, which can impact its functionality and accessibility.
- PITA: It’s not easy to just ‘use’ needing logins, downloads and a 15 year old child to show you how to work it.
Strengths:
- Specialised in content creation: Excels in generating marketing copy, blog posts, and other content-related tasks.
- User-friendly interface: Designed for ease of use, with intuitive tools and templates for content creation.
- Strong SEO capabilities: Tailored for SEO optimisation, helping users create content that ranks well in search engines.
Weaknesses:
- Limited scope: Primarily focused on content creation, with less versatility in other applications like technical writing or code generation.
- Subscription cost: Can be expensive for individual users or small businesses.
7. Hugging Face’s Transformers
Strengths:
- Wide range of models: Offers a variety of pre-trained models for different tasks, from text generation to image classification.
- Strong community and support: Active community and extensive documentation make it accessible for developers.
- Flexibility: Allows for easy customization and fine-tuning for specific tasks.
Weaknesses:
- Requires technical expertise: (See PITA above) More suitable for users with technical knowledge, as it involves some setup and configuration.
- Performance variability: The performance can vary significantly depending on the specific model and configuration used.
- Probably the weirdest name of the bunch: Llama yes, cute. Chat – boring but yes. Hugging face? I’m getting Alien movie vibes.
Do you use AI already? Leave a comment below.



